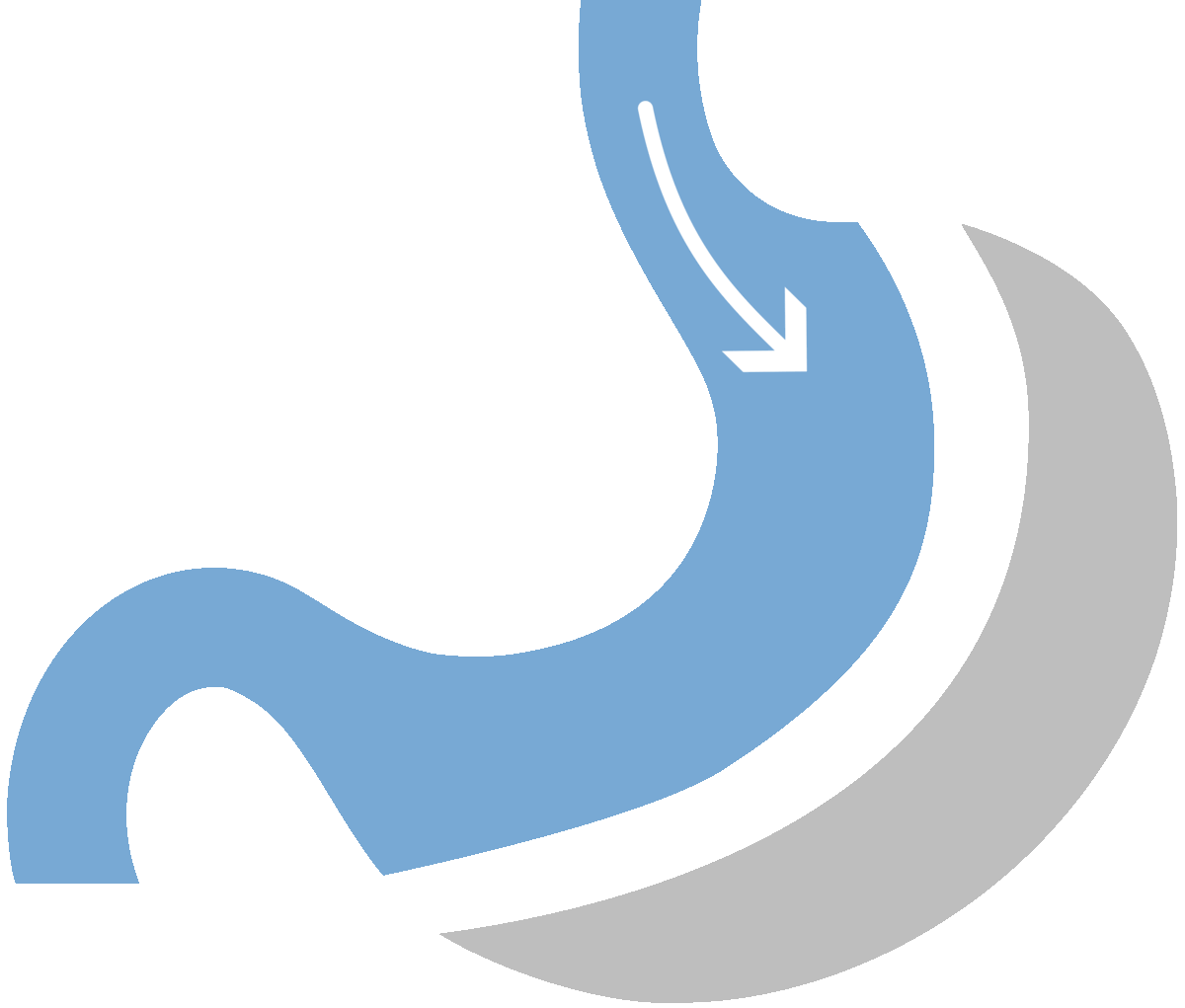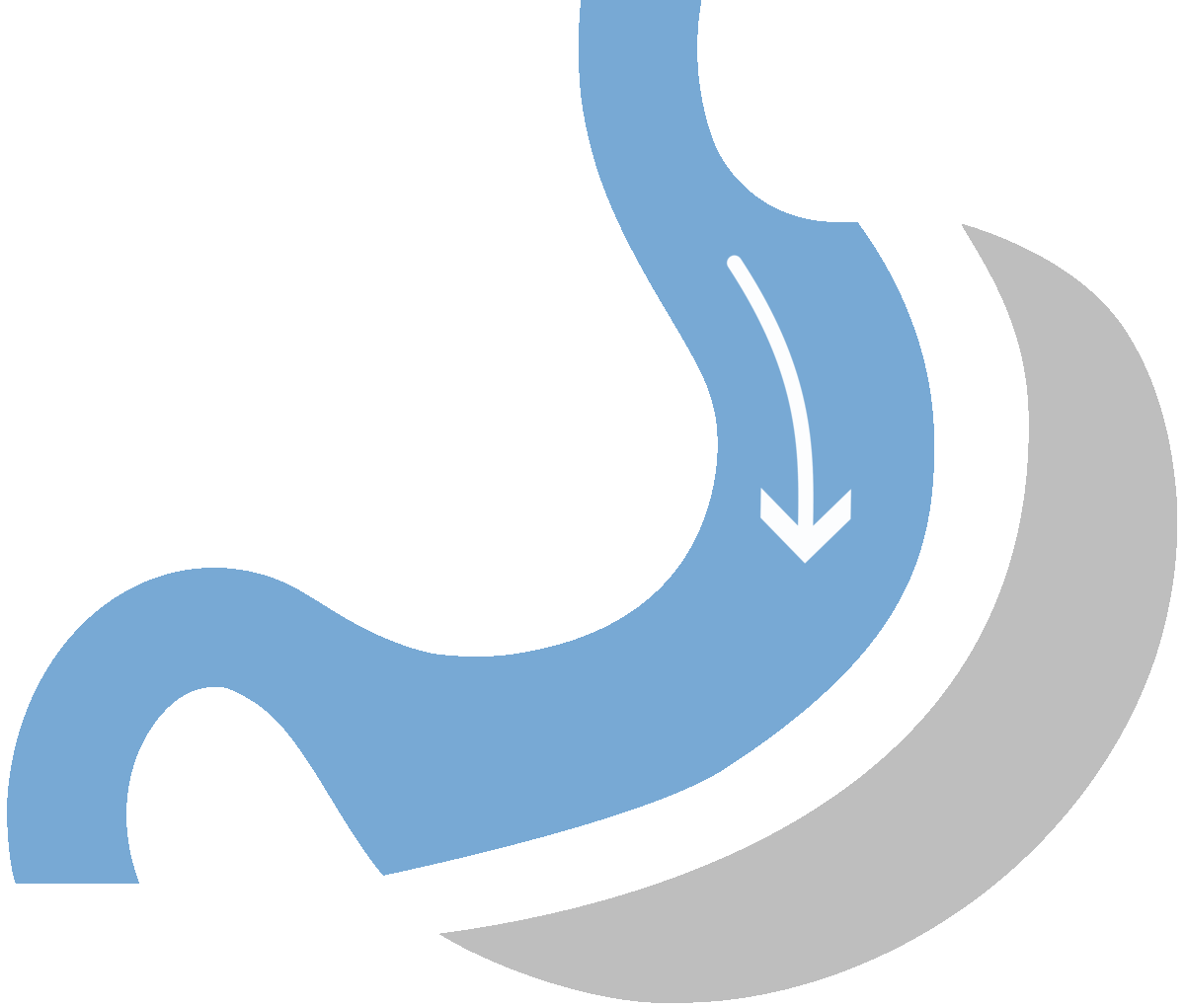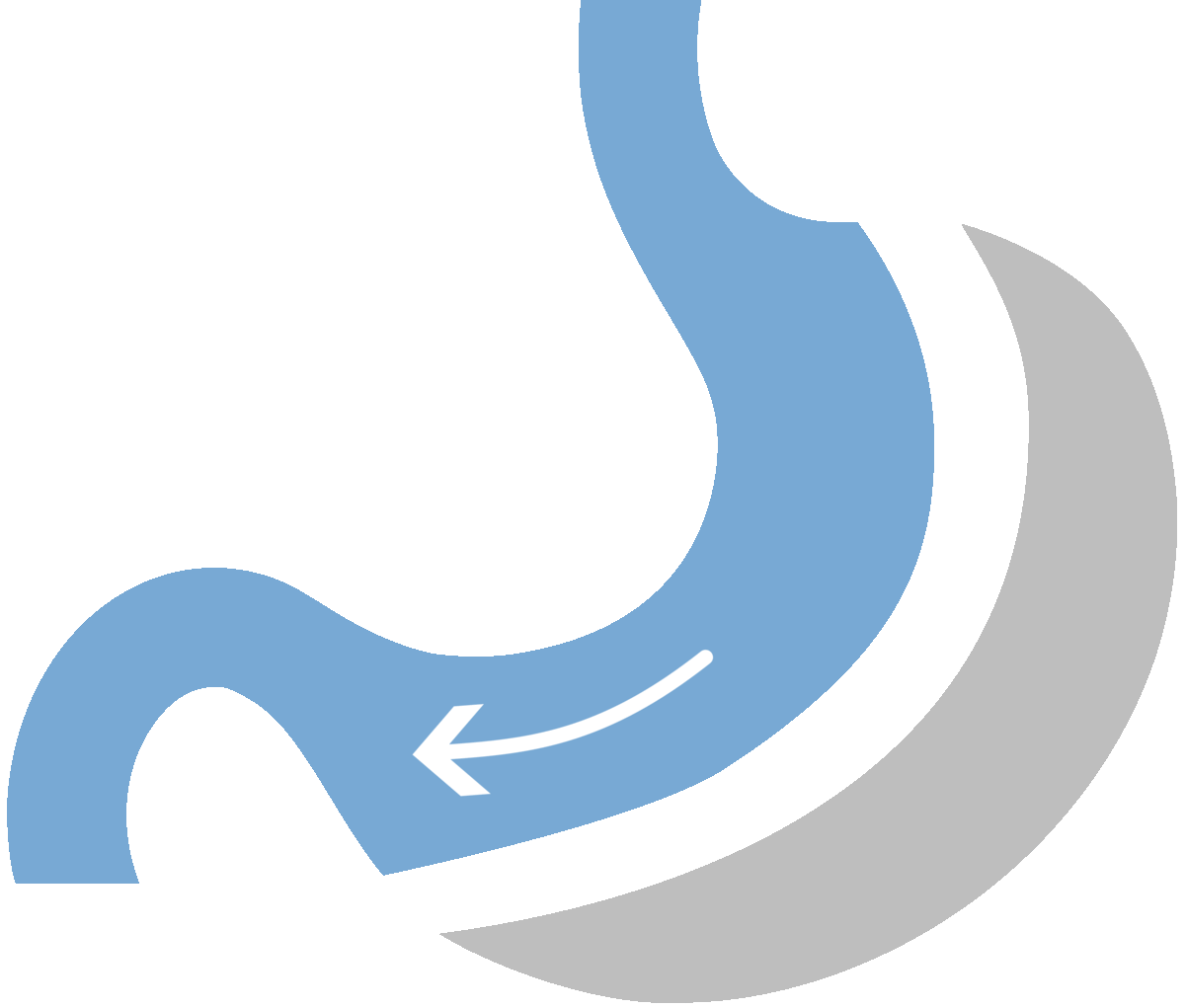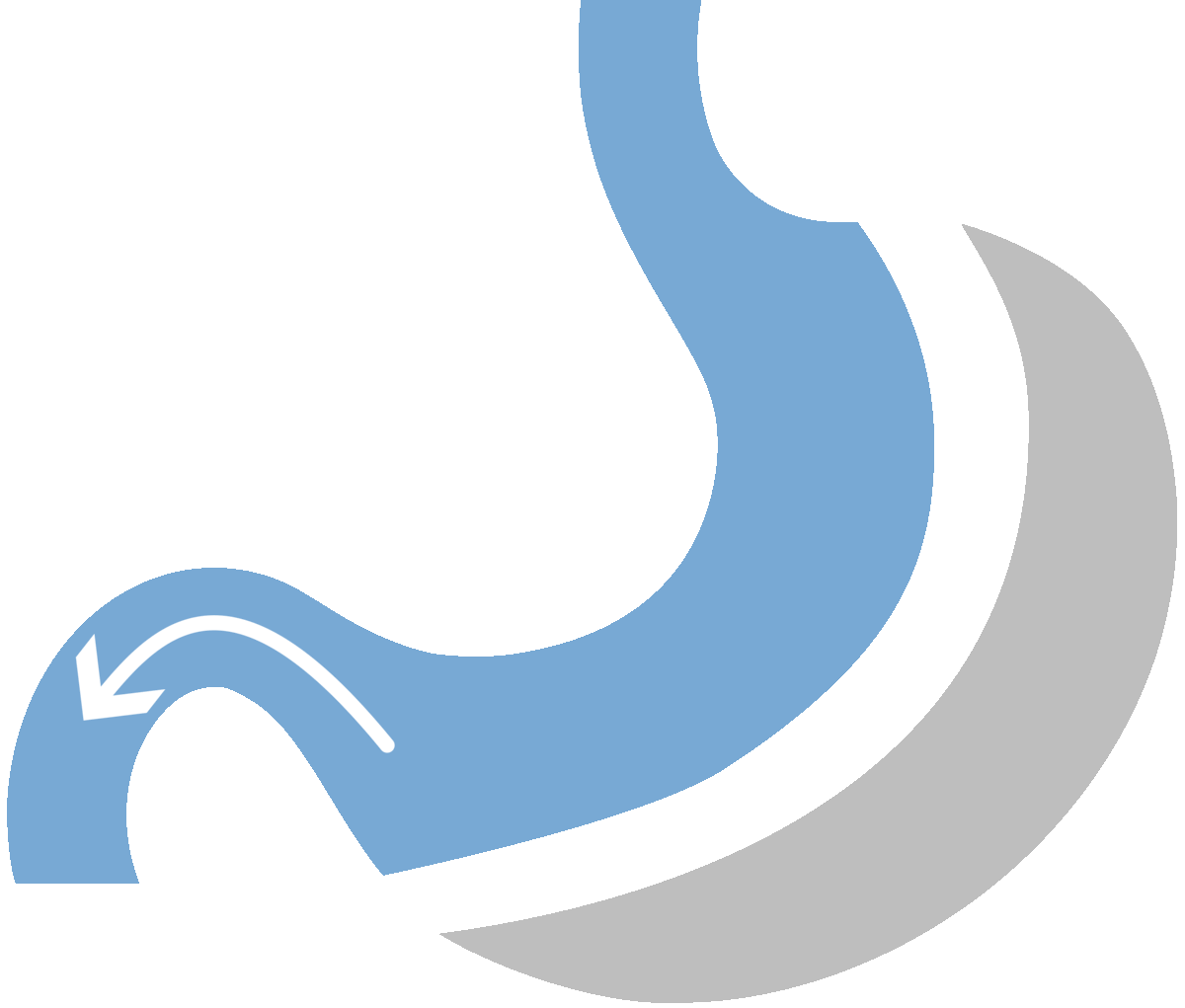
What is Gastric Sleeve
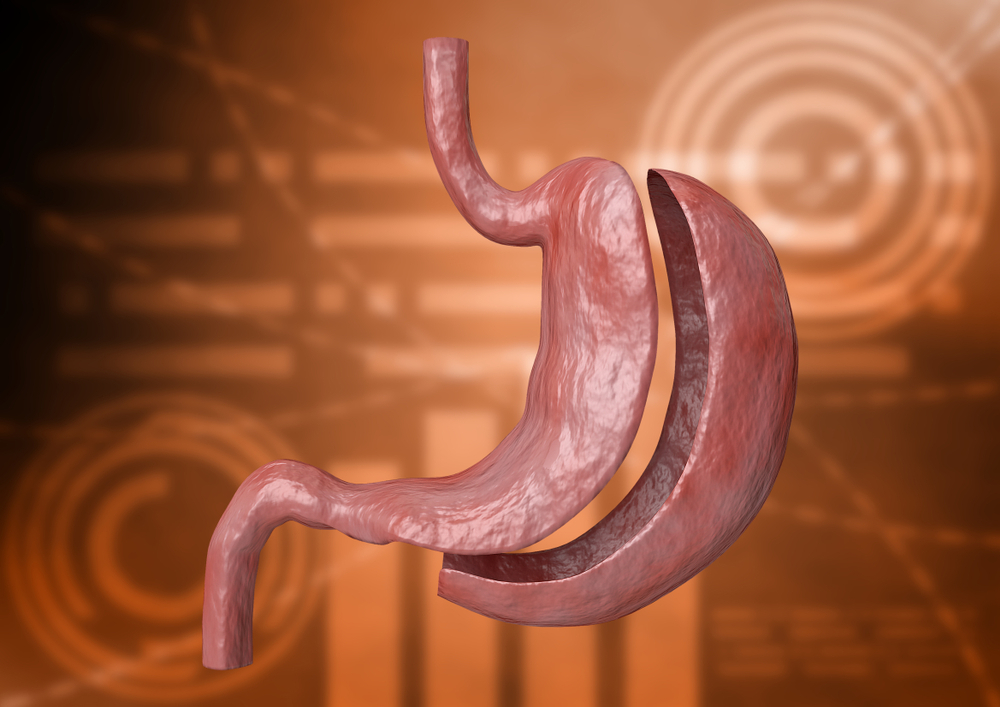
Gastric sleeve surgery, formally known as sleeve gastrectomy, stands out as a highly favored and minimally invasive approach to weight loss. This procedure involves the removal of a substantial portion of the stomach, resulting in the formation of a smaller, banana-shaped stomach.
This anatomical alteration plays a pivotal role in curbing food intake, as the reduced stomach capacity inherently limits the amount of food an individual can consume. As a result, patients experience significant weight loss, making gastric sleeve surgery particularly effective for those dealing with moderate to severe obesity.
Beyond its impact on weight, gastric sleeve surgery has proven benefits for overall health improvement. The procedure often leads to positive outcomes in managing and even resolving obesity-related health conditions. By achieving substantial weight loss, patients may experience enhanced metabolic function, reduced risk of cardiovascular issues, and improved blood sugar control.
Additionally, the minimally invasive nature of the surgery contributes to quicker recovery times and fewer postoperative complications, making gastric sleeve surgery an appealing choice for individuals seeking a comprehensive and sustainable weight loss solution.
How does it Work?
During laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery, a surgeon makes small abdominal incisions and employs a laparoscope—a slender tube housing a camera and thin instruments—to perform the procedure under general anaesthesia. Typically lasting 1-2 hours with a brief 2-day hospital stay, patients can anticipate a substantial reduction of up to 60% in excess weight within 1-2 years post-surgery. This transformative process involves two key mechanisms: physical/restrictive and physiological.
The physical/restrictive aspect entails suturing the stomach along its length, creating a tube-shaped structure that restricts food volume, induces a feeling of fullness, and reduces caloric intake. Simultaneously, about two-thirds of the stomach is removed, curbing the production of ghrelin—a hunger-inducing hormone—resulting in decreased appetite and earlier satiety.
Unlike gastric bypass, the gastric sleeve does not alter the food passage route in the gastrointestinal system, minimizing the impact on nutrient absorption and lowering the risk of malnutrition. This procedure, with its shortened hospitalization period, positively influences hormones regulating hunger, fullness, and blood glucose levels, offering a comprehensive and effective solution to weight loss and improved well-being.
Who is considered as an eligible candidate for Gastric Sleeve?
Laparoscopic Gastric Sleeve Surgery is a recommended option for individuals meeting specific criteria, ensuring its suitability for those seeking effective weight loss solutions. Eligibility often includes a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 35 or higher, indicating obesity (class II or higher).
Additionally, individuals with a BMI of 30 or higher may qualify if accompanied by obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, heart disease, or cholesterol issues. Previous unsuccessful attempts at weight loss through diet, exercise, and non-surgical methods contribute to candidacy, emphasizing the procedure's role in cases where conventional approaches prove ineffective. Further, past medical and surgical history can influence eligibility, underscoring the importance of a pre-surgery consultation to determine individual suitability for Laparoscopic Gastric Sleeve Surgery.
The benefits of Laparoscopic Gastric Sleeve Surgery are multifaceted, offering individuals a comprehensive and effective approach to weight loss. First and foremost, the procedure presents a lower risk profile due to its simplicity, focusing solely on reducing stomach size. This results in fewer complications during and after surgery compared to more intrusive procedures. The operation is less invasive, avoiding changes to the gastrointestinal food passage route and minimizing the risk of malnutrition, particularly when compared to gastric bypass surgery.
On the medical front, Gastric Sleeve Surgery significantly reduces obesity-related illnesses such as high blood pressure, stroke, type 2 diabetes, cholesterol issues, infertility, sleep apnea, asthma, and cancer. Additionally, it contributes to long-term control of type 2 diabetes, potentially leading to reduced dependence on medications or their elimination altogether.
Physiologically, individuals experience less hunger and an increase in energy, along with benefits like the elimination of back and joint pain, improved mobility, decreased depression, enhanced breathing, and increased overall energy levels. Psychologically, the surgery brings about dramatic improvements in overall health and quality of life, fostering an enhanced self-image, increased self-confidence, and greater satisfaction in engaging in a wider range of activities with friends and loved ones. It's crucial to note that individual results may vary, and sustainable outcomes are best achieved through a combined approach, incorporating lifestyle changes for optimal and enduring results.
Preparation for gastric sleeve surgery involves meticulous steps in the weeks and days leading up to the procedure. Weeks before surgery, comprehensive medical screening, lab tests, imaging assessments, psychological evaluations, nutritional assessments, and pre-counselling sessions are conducted to determine the suitability and fitness for the surgery.
A crucial element in this preparatory phase is adhering to a pre-surgery weight loss diet, which is low in fat and carbohydrates. This dietary regimen aids in reducing glycogen levels and shrinking the liver, creating optimal conditions for the operation. Additionally, abstaining from caffeinated drinks at least a week before the surgery is recommended. The dietary focus in the week preceding the surgery should shift towards increased fluid intake, vegetables, and fruits.
As the surgery date approaches, it becomes imperative to cease smoking, alcohol consumption, caffeine intake, and the consumption of heavy, unhealthy meals. Avoiding aspirin, ibuprofen, and other blood-thinning medications is crucial. It's essential to inform the doctor about any medications being taken beforehand. Furthermore, a fasting period is observed, refraining from eating or drinking anything after midnight the night before the scheduled surgery. These meticulous preparations contribute to a smooth and successful gastric sleeve surgery.
Recovery after gastric sleeve surgery varies among individuals, but certain key aspects are essential to understanding the process. Following the procedure, patients typically stay in the hospital for 2-3 days for proper healing, rehabilitation, and progress monitoring. Those who undergo laparoscopic procedures may return to work in less than a week, although engaging in intense physical activities is not advisable during this early phase.
Post-surgery, meticulous follow-up care is crucial. Dietary adjustments play a pivotal role, guided by a nutritionist who will assist in reintroducing foods gradually to accommodate the reduced stomach size. The transition involves phases such as a clear liquid diet within 24 hours post-surgery, followed by a progression to a full liquid diet, soft food diet, and eventually a return to a regular diet in the subsequent weeks. Patients are advised to reduce certain foods, particularly simple sugars, to prevent dumping syndrome. Proper chewing, avoiding drinking 30 minutes before or after meals, and adherence to dietary recommendations are essential to prevent complications like constipation, dehydration, diarrhea, or, in rare cases, gastric acid leakage.
Supplements, including Vitamin B12, iron, and multivitamins, may be recommended during follow-up visits to address nutritional needs. Patients should promptly report any unusual symptoms or complications to their doctors, such as fever, painful wounds, respiratory issues, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal, chest, shoulder, or leg pain.
During the weight-loss phase, temporary side effects like body aches, dry skin, mood changes, and hair thinning may occur. As weight stabilizes, these issues typically resolve, and weight loss continues for about a year until it stabilizes at the body's optimum BMI. Adhering to post-surgery guidelines and seeking prompt medical attention for any concerns contribute to a successful recovery journey.
Before contemplating gastric sleeve surgery, it's crucial to understand the potential risks associated with bariatric procedures, with variations based on the patient's health. Some uncommon issues that can be managed fairly easily include minor wound or skin infections, excess/loose skin, vomiting or nausea, acid reflux (heartburn), the development of gallstones or gallbladder disease, and nutritional deficiencies due to food bypassing the stomach.
Complications that could necessitate re-operation include internal bleeding, blood clots in the legs or lungs, gastric leaks, and risks associated with laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, such as deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, iron, metabolic bone disease, and chronic anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency. General risks of surgery, such as bleeding, infection, and blood clots, may occur. Over time, difficulty absorbing certain nutrients, narrowing of the stomach sleeve, and potential exacerbation of heartburn or reflux are also possible concerns.
The decision to undergo gastric sleeve surgery should be made after a thorough discussion with our team of professionals, considering individual health and potential risks. Despite potential disadvantages, the data from a large number of patients nationwide shows that the risk of death is relatively low, highlighting the overall safety and benefits of weight loss surgery in addressing obesity-associated medical problems.
GASTRIC SLEEVE VS GASTRIC BYPASS
Gastric sleeve surgery, or sleeve gastrectomy, is a preferred and minimally invasive method for weight loss. It entails removing a substantial portion of the stomach, creating a smaller, banana-shaped stomach. This reduces stomach capacity, limiting food intake and resulting in significant weight loss—especially effective for those with moderate to severe obesity. Besides weight reduction, the procedure positively impacts overall health by managing or resolving obesity-related conditions. Performed laparoscopically, the surgery involves small incisions, a camera-equipped laparoscope, and typically lasts 1-2 hours with a brief hospital stay. The two key mechanisms, physical/restrictive and physiological, induce a feeling of fullness and reduce caloric intake. Importantly, unlike gastric bypass, it maintains the natural food passage route, minimizing nutrient absorption impact and malnutrition risk.
Gastric bypass, a widely embraced and effective weight loss method, involves creating a smaller stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine. In contrast to the less intrusive gastric sleeve, it achieves substantial weight loss by constraining stomach capacity and altering the digestive pathway. Success depends on strict adherence to a structured post-surgery dietary regimen, emphasizing nutrient-dense, portion-controlled meals. Gastric bypass addresses obesity-related health conditions holistically but demands disciplined commitment to prevent complications. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery includes small belly incisions, taking 1-3 hours with a 3-day hospital stay. Weight loss is gradual, taking 1.5 to 2 years, shedding up to 70% of excess weight. Eligibility requires a BMI over 40 or over 35 with obesity-related conditions.
In essence, the choice between gastric sleeve and gastric bypass depends on individual health conditions and the commitment to post-surgery lifestyle changes. While both procedures offer effective weight loss, the gastric sleeve maintains the natural digestive route, providing simplicity and sustainability. In contrast, gastric bypass achieves more significant weight loss but necessitates rigorous adherence to dietary guidelines and alters the digestive pathway.
The process to get you started on your weight loss journey
Non - Surgical Approaches
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential for overall well-being.
While weight loss journeys vary from person to person, there are numerous safe and effective methods available, both surgical and nonsurgical.
Here, we explore different approaches to healthy weight loss.

The Endoscopic Sleeve, or Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG), is a minimally invasive bariatric procedure reducing stomach size through internal suturing, mimicking surgical sleeve gastrectomy effects. This non-surgical technique facilitates significant weight loss and health improvement, providing an effective alternative to traditional methods.
Endoscopic Sleeve

Gastric injections, a non-surgical procedure, involve injecting botulinum toxin into the stomach lining, temporarily paralysing muscles to curb hunger and induce early satiety. Despite being less invasive, their effects are transient, lasting only a few months in the pursuit of temporary appetite control.
Gastric Injections

Injectable weight loss treatments are administered via injections, impact appetite control, resulting in reduced food intake and potential weight loss. These injections serve as a valuable tool for individuals to effectively manage their weight and achieve their desired health outcomes.
Weight Loss Injectables

The Allurion Balloon, a non-surgical weight loss solution ingested as a pill and inflated in the stomach, induces fullness, reducing food intake and promoting weight loss. It provides an appealing, convenient alternative to traditional bariatric surgeries for those seeking effective, minimally invasive options.
Swallowable_Allurion Balloon

Adjustable balloons offer a unique advantage in weight management, allowing modification after placement. This adaptability empowers healthcare professionals to fine-tune stomach filling, optimising personalized weight loss strategies. Their versatility makes them an ideal choice for addressing patients' specific needs in effective weight management.
Adjustable Gastric Balloon

Endoscopic balloons, inserted into the stomach through an endoscope, induce fullness, occupying space and curbing food consumption. This non-surgical, minimally invasive method is favoured for temporary weight loss assistance in medical management, offering a practical option for those seeking effective intervention.
Endoscopic Gastric Balloon


Surgical Weight Loss
Gastric Sleeve
Gastric sleeve surgery, or sleeve gastrectomy, is a widely favoured, minimally invasive weight loss solution. Removing a significant part of the stomach forms a smaller, banana-shaped stomach, curbing food intake, aiding weight loss, and enhancing health in cases of moderate to severe obesity.
Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass, a proven weight loss approach, forms a small stomach pouch and redirects the small intestine. While more invasive than the gastric sleeve, it effectively induces weight loss and improves health conditions, demanding rigorous post-surgery dietary adherence for optimal outcomes.
Mini Gastric Bypass
The mini gastric bypass streamlines the traditional process, establishing a smaller stomach pouch directly linked to the small intestine. Balancing effectiveness and invasiveness, it delivers substantial weight loss and health benefits, demanding lifelong dietary adherence for success, making it a preferred choice.
Duodenal Switch
The duodenal switch, a preferred weight loss surgery for severe obesity, involves stomach reduction and small intestine rearrangement to limit calorie absorption, leading to significant weight loss. Despite its effectiveness, careful dietary management is crucial, making it suitable for those unsuccessful with other treatments.
FAQs
Obesity surgeries are evaluated based on body mass index, previous surgeries, previous medical history, amount of weight loss desired as well as financial implication – are the variables that help determine this.
It is dependent on an individual’s body mass index (BMI) and the presence of any co-morbidities. You may qualify for surgery if you have a BMI of 40 or greater, or if your BMI is at least 35 with other obesity-related health problems e.g. diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
Usually 1-4 days of stay in the hospital. Problems that may occur during the preoperative evaluation and postoperative recovery period may determine this period.
Communication with your team and following your doctor’s instructions can prevent majority of the complications. Some include – dumping syndrome, dehydration, and nutrient deficiencies but can be avoided if the correct diet is followed and supplements.
We will transition you from liquid diet to solid diet gradually. High carb, sugary fluids and generally junk meals are to be reduced or completely avoided for better results, minimal side effects and sustainability of weight loss
After leaving the hospital, heavy activities should be reduced. The patient should not lift heavy loads for about 6 weeks.
TESTIMONIALS
Why Choose Halcyon

Experience a transformative journey with holistic programs, integrating customized meal plans, targeted fitness routines, and behaviour modification strategies for sustained well-being and optimal health.
Comprehensive Approach

Harness the power of advanced tools and technologies to precisely track your progress, optimize workouts, and achieve efficient fat loss, ensuring a data-driven and results-focused approach.
Cutting Edge Technology

Witness real-life success stories as testimonials to our commitment, showcasing significant weight loss transformations achieved through our dedicated programs and unwavering support system.
Proven Results
We inspire hope to health and
wellbeing to every patient.
456 +
Successful Surgeries
56,464 +
Patients Treated
95,613 +
241 Medications (Everyday)
Book an Appointment
5th Avenue Office Suites, 7th Floor Suite 5-8
Ngong Road Upperhill Area, Nairobi